
API

1️⃣ What is an API?
The API (Application Programming Interface) is a set of rules and protocols that allow different software applications to communicate and interact with each other.
API allows real-time data transfer, whereas sending CSV files requires the data to be inputted manually, which can result in delays between file creation and processing, as well as a higher risk of human error.
With an API connection, it is possible to automate the data import process. Systems can be configured to connect directly to the API and retrieve the necessary data at regular intervals, without human intervention.
Did you know?
The use of an API can offer advanced security measures. API connections can be protected by authentication mechanisms such as API keys, access tokens. Additionally, data is transmitted securely through protocols such as HTTPS (Secure HTTP).
Different Types of APIs
Server-side APIs are used to enable applications to communicate with the server.
Client-side APIs are used to enable applications to communicate with client applications.
Did you know?
The RESTful API is one of the most commonly used types of APIs. It uses standard HTTP methods such as GET, POST, PUT, and DELETE to interact with data. The RESTful API is very flexible and can be used for many applications.
The Architecture Behind an API
JSON is designed to be easy to read and write for humans, while also being easy to parse and generate on the code side. It is often used in APIs to represent and transmit structured data.
HTTP defines different request methods, such as GET, POST, PUT, DELETE, which allow clients to specify the action they want to perform on server resources.
Did you know?
HTTP uses status codes to indicate the result of the request. For example, the code 200 or 201 indicates that the request was successful, the code 400 or 404 indicates that the requested resource was not found, etc.
2️⃣ Requests (GET & POST)
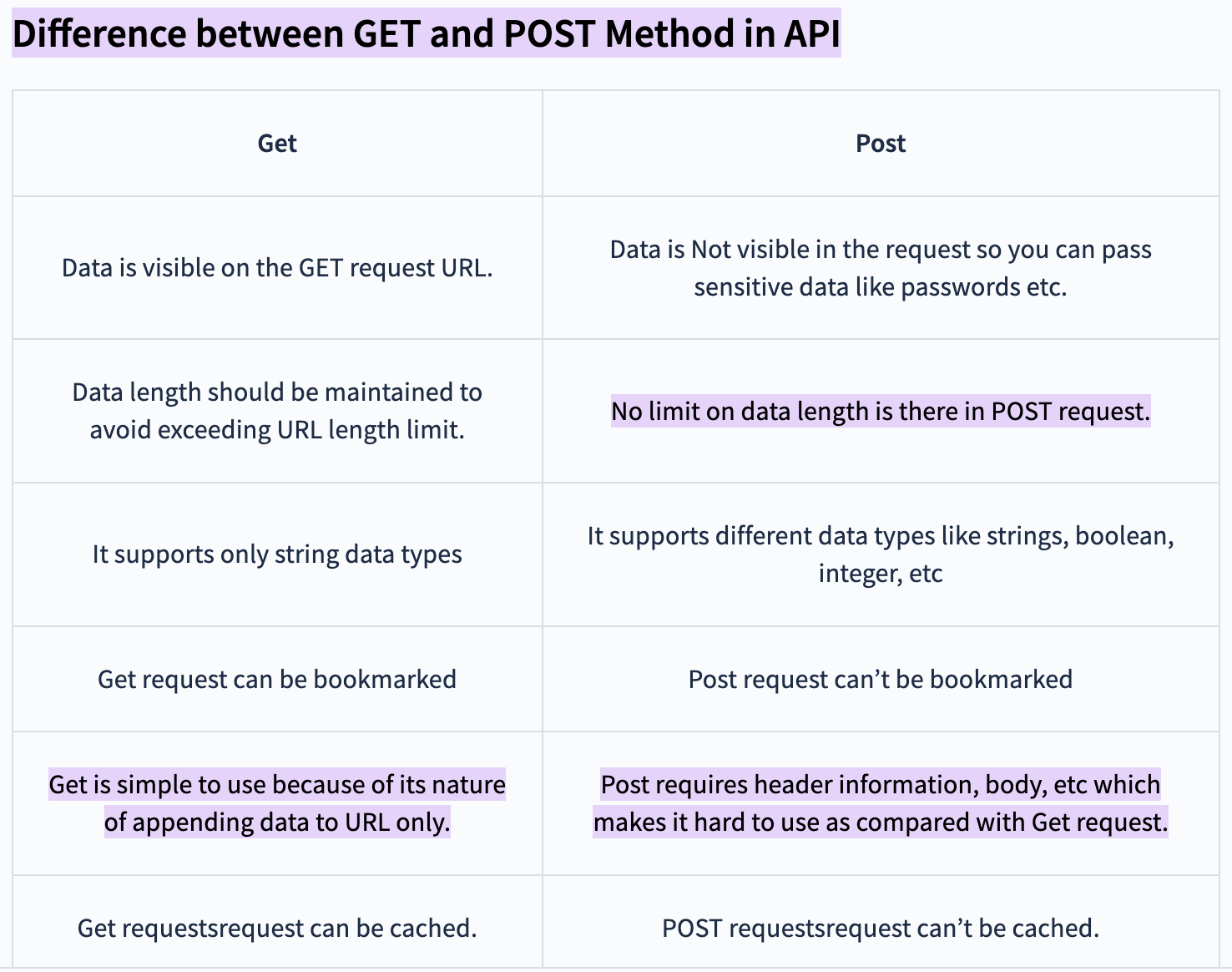
1️⃣ A GET request is used to retrieve data. When a GET request is sent, the client specifies the URL of the resource it wants to reach. Query parameters can also be included in the URL to filter results or specify search criteria.
Example of a GET request:
GET /api/users?id=123
Note: Brands can extract data directly from the platform themselves (CSV). Obviously, the extracted data is part of a specific scope of data (LCA results, traceability, notes, links, etc.). If clients have specific data needs, we can perform custom extractions.
2️⃣ A POST request is used to submit data to the server to create a new resource or perform a specific action. When a POST request is sent, the data to be sent is included in the request body. Unlike the GET request, the POST request can have a side effect, such as creating a new resource or modifying an existing resource.
Example of a POST request:
POST /api/users
Content-Type: application/json
{
”name”: “John Paul”,
”email”: “JohnPaul@example.com”
}
Note: It is important to note that GET and POST requests are only not the only request methods available in the HTTP protocol. There are also other methods such as PUT, DELETE, PATCH, etc., which are used for other types of operations in the context of an API.
3️⃣ Status Codes
The HTTP status code 400 (Bad Request) is returned by a server when the request sent by the client is incorrect or malformatted. This can occur if the request parameters are missing, if the data sent is not valid, or for other error-related reasons.
4️⃣ Advantages of APIs
One of the main advantages of an API is that it allows developers to create applications more quickly. By using the API, developers do not need to create all the necessary features for their application from scratch.
Instead, they can use existing features provided by the API to do the job.
The API also allows applications to communicate with each other.
For example: an e-commerce application can use the API to interact with a payment application. This allows users to place an order and pay for their purchases without having to leave the e-commerce application.
5️⃣ Conclusion
❓ F.A.Q.
As a brand, what do I need to prepare to be ready for the launch of a project?
You need to access the Data Model (for API connection) or the Brand Data Collection (Excel).
The Data Model lists all the data that you can send/push to us based on the chosen module. The Home tab explains how to proceed and navigate through the file.
Certain data is required, indicated by checked boxes (or marked as "TRUE") in column J.
The Data Model contains the same information as the API documentation and provides a better understanding for non-IT teams regarding data mapping and transcodification to be performed.
To follow the API documentation, refer to the project type indicated in the Data Model and the corresponding tab, line 3. The data should be sent in .json format.
1) Identify the source of the data requested by Fairly Made®.
Where are they stored in the brand's IT system?
For IT & Business teams: Preliminary meetings and work coordination.
- Transcoding = Mapping the brand's list (enum.) to Fairly Made®'s lists (enum. OR taxonomy lists described in the data model).
PLM / ERP Manager: Perform the transcoding.
- Launch the testing phase via API and/or Excel with a small number of products. Both tests can be conducted simultaneously.
IT / Digital Project Manager: Perform tests on the Sandbox and validate the business rules with Fairly Made®.
If launching through API, we will also provide the API documentation.
If you are ready to send/push data via API, please contact us so that we can provide you with access tokens to test on the Sandbox.
How does the API and our data import work?
On the Tech side, we have switched data import from CSV/Excel directly to the API. Basically, we imports the CSV file (BDC) and the API reads all the information transmitted and tells us whether a given product is accepted or not (and why). This is for data relating to suppliers, packaging, products and components. The Tech team runs the CSVs through a dedicated import script that reprocesses the information. The same goes for the API made available to our customers, but we'll come back to that later.
’Instant’ Brand Data Collection : brands push data via API directly through our interface. They receive validation and/or error messages indicating whether the data has been received and, if so, what is wrong with it.
This makes it possible to have clean data and for engineers/analysts to work with customers on points so that they can concentrate on the rest.
We can also transmit almost instantaneously: the product sheet and the QR code that will be loaded (information and analysis results) later.As a reminder, the order in which data is sent via API is as follows:
- Supplier
- Packaging (may come at the end if the customer does not have this information)
- Product
- Component
Why is this?
You have to think of it as a funnel: one data package needs another in order to exist. Component data does not exist without product data, which is itself linked to packaging and supplier data.
(Unique Product Reference - Product Color Code - Product Collection: the triplet that makes a study unique for a reference).
What is the API documentation?
The API documentation is the technical translation of the Data Model.
Fairly Made API documentation:
Overview: This section provides a general introduction to the API, explaining its purpose, key features and use cases. It may also include information on registration, authentication and requirements for accessing the API.
Endpoints: An API is made up of endpoints, which are specific URLs for accessing different API features or resources. The API documentation details each available endpoint, explaining its use, the necessary parameters, the HTTP methods supported (such as GET, POST), and the expected responses.
Request examples: This section presents concrete examples of requests that can be made to the API. These examples often include request parameters, required headers and accepted data formats.
Response examples: Response examples show the data formats returned by the API in response to requests. This can include examples of HTTP status codes, JSON data structures, response headers and other relevant information.
Errors and error handling: This section explains common errors that can occur when using the API, along with the associated error codes and how to handle them correctly.
Specifically:- A description of the API, its functionality and purpose.
- The API URLs and endpoints available to developers for making requests to the API.
- HTTP request methods supported by the API, including GET, POST, and examples of corresponding requests and responses.
- Acceptable parameters for each endpoint, and requirements for API calls.
- API response formats, which may be in JSON format.
- Information on authentication and authorisation for developers wishing to access the API.
- Common errors that may occur when using the API and associated error messages.
- Authentication is required to access the API, and developers can authenticate using an access token.
- The documentation also provides code examples to help developers understand how to use the API.
As mentioned earlier, the Batch Import is a character string used to identify a packet of data that has been sent together. It is useful for both the brand and Fairly Made® to identify a batch, a shipment, a packet of information that has been sent. It is used to track and trace the data sent.
Data to be sent in Delta mode, i.e. to avoid the brand sending us all the data every time. This can have an impact on the load on our infrastructure connection. It can also create duplicate products. How often? Batch imports at a regular rate for each push?
By a trigger defined by them (e.g. Go Production by the brand) Data can be sent in specific waves. To be agreed with the tech & engineer / analyst.
How often should the data be sent?
To be determined according to the brand's internal organisation. In general, we work in waves for each season. However, it's the brand that takes care of synchronising and sending the data. It's not Fairly Made that 'PULLS' the data into the brand system. It is the brand that "PUSHES" the data into the Fairly Made systems.
How long does the process take? What are the different steps?
Typical process:
- Brand Data Collection: 2 weeks
- Supplier Data Collection: 8 weeks
- Environmental Performance Analysis : 3 weeks (LCA)
- Formatting & Publication of Results: 1 week
(The process is shortened if connected via API)
Explanation of the process for a large project:
- Collection of brand data (approx. 3 weeks)
- This is where we collect your information so that we can launch our analysis via an API connection to your PLM.
- The essential information we need is: the composition of your products, the name and email address of your Tier 1 manufacturer, the weight of the product (for the LCA).
- Data collection from suppliers (7-8 weeks)
- Contact your suppliers to collect their traceability information.
- Life cycle analysis (2 weeks)
- B2C communication installed (basically instantaneous)
Total: approx. 4 months
Stages :
Kickoff, Onboarding of users, Data collection (Brand + Factories); Analysis; Online publication of results
From collection of brand data to delivery of studies on the platform: between 14 and 28 weeks.
Brand Data Collection:
- Configuration of brand parameters
- Collection of brand data (directly via your PLM with API)
Factory Data Collection
- Collection of data from factories.
- Technical characteristics of each product
Analysis
- Audit of existing certifications.
- Assessment of traceability.
Product life cycle analysis (ISO 14044)
Processing & publication of results
- Generation of URLs, QR codes and widgets.
- Support for your environmental communication teams
Throughout the process, you will be supported by : 1 textile engineer responsible for your study & 1 Customer Success Manager.